# Elasticsearch Configuration
# Introduction
Elasticsearch is a powerful distributed search and analytics engine, built on Apache Lucene, designed for scalability and real-time data processing. It excels at fast full-text search, complex querying, and handling large volumes of data with high availability. Elasticsearch is widely used for applications requiring robust search capabilities, from real-time logging and analytics to e-commerce product search and personalized recommendations.
In this section, we will explain how to configure Elasticsearch for indexing products from the database.
# Environment Setup
Before we proceed, make sure you have Elasticsearch (opens new window) installed on your system. By default, Elasticsearch uses port 9200. We will be using the same port for our configuration.
To verify if Elasticsearch is installed successfully on your system, open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:9200. If you see the following output, it means Elasticsearch is installed:
{
"name" : "webkul-pc",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "suPotT8zQjCOlq9dteWKyQ",
"version" : {
"number" : "8.6.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "deb",
"build_hash" : "2d58d0f136141f03239816a4e360a8d17b6d8f29",
"build_date" : "2023-02-13T09:35:20.314882762Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "9.4.2",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "7.17.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "7.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Alternatively, you can use the curl command:
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:9200'
This command should return a similar JSON response, confirming Elasticsearch's availability and version details.
# Configuration Setup
Note
This configuration is for the latest version 2.1.0
To configure Elasticsearch, you can set the necessary value in the config/elasticsearch.php file of your project.
# Default Connection
The connection key specifies the default Elasticsearch connection to use when building a client.
/**
* Here you can specify the connection to use when building a client.
*/
'connection' => 'default',
# Available Connections
You can define multiple Elasticsearch connections with different configurations under the connections array.
/**
* These are the available connections parameters that you can use to connect
*/
'default' => [
'hosts' => [
env('ELASTICSEARCH_HOST', 'http://localhost:9200'),
],
'user' => env('ELASTICSEARCH_USER', null),
'pass' => env('ELASTICSEARCH_PASS', null),
],
# API Key Authentication
You can connect with API key authentication by setting the api key instead of the user and pass keys.
'api' => [
'hosts' => [
env('ELASTICSEARCH_HOST', null),
],
'key' => env('ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY', null),
],
# Elasticsearch Cloud
You can connect to Elastic Cloud with the Cloud ID using the cloud key
'cloud' => [
'id' => env('ELASTICSEARCH_CLOUD_ID', null),
/**
* If you are authenticating with API KEY then set user and pass as null
*/
'api_key' => env('ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY', null),
/**
* If you are authenticating with username and password then set api_key as null
*/
'user' => env('ELASTICSEARCH_USER', null),
'pass' => env('ELASTICSEARCH_PASS', null),
],
# CA Bundle
The caBundle option allows you to specify the path to the CA Bundle certificate if required for SSL/TLS connections.
/**
* If you have the http_ca.crt certificate copied during the start of Elasticsearch
* then the path here
*
* @see https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/php-api/current/connecting.html#auth-http
*/
'caBundle' => null,
# Retries
The retries option controls the number of times the client will retry requests. By default, it retries as many times as there are nodes in the Elasticsearch cluster.
/**
* By default, the client will retry n times, where n = number of nodes in
* your cluster. If you would like to disable retries, or change the number,
* you can do so here.
*
* @see https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/php-api/current/set-retries.html
*/
'retries' => null,
Not
Below are the essential configuration details for setting up Elasticsearch in version 2.0.0
To configure Elasticsearch, you can set the necessary key-value pairs in the .env file of your project.
Open the .env file and add the following lines:
ELASTICSEARCH_PORT=9200
ELASTICSEARCH_HOST=localhost
Save the file and run the following command to cache the configuration:
php artisan config:cache
Now your environment is set up and ready to index products.
If you encounter any issues, you can directly set the configuration in the config/elasticsearch.php file:
'hosts' => [
[
'host' => env('ELASTICSEARCH_HOST', 'localhost'),
'port' => env('ELASTICSEARCH_PORT', 9200),
// Additional configuration options can be added here
]
]
# Indexing
After setting up the environment and configuration, new products will be automatically indexed when created.
To index existing products, run the following command:
php artisan indexer:index
This command will index all the data from the product_flat table to the Elasticsearch index.
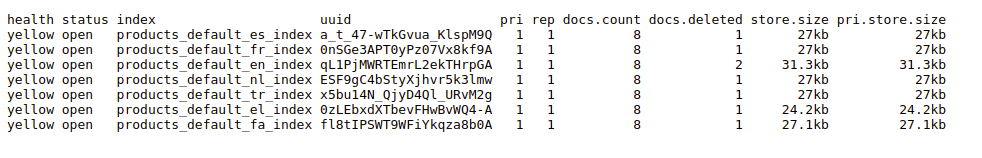
# Checking Indexes
To check if your products have been indexed successfully, open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v. You should see information about the imported index.
Alternatively, you can use the curl command:
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v'
The output will provide details about the product index:
Output
By following these steps, you have successfully configured Elasticsearch and indexed your products.
